Real-Time Ultrasound
Physiotherapy Real-Time Imaging for the Lumbar Spine.
Complete Wellness Physiotherapy provides real-time ultrasound imaging of the stabilising muscles of the lumbar spine. Real-time ultrasound (RTU) imaging provides vital improvements in the accuracy and effectiveness of the treatment of low back pain. Simply put, the use of RTU imaging takes the guesswork out of both the cause of low back pain and its most effective management.
The Stabilising Muscles of the Lumbar Spine
Research tells us that following injury to the lumbar spine (low back), the muscles that stabilise the spine become significantly inhibited (i.e. they switch off)
The subsequent weakening and loss of control of the stabilising muscles often leads to poor or incomplete recovery from the injury and the development of chronic or recurrent low back pain.
Exercises for the Stabilising Muscle
The stabilising muscles of the lumbar spine do not usually recover spontaneously following an episode of low back pain. Therefore, specific exercises are required to stimulate their redevelopment
Research now clearly demonstrates that non-specific global exercises, such as fit ball programmes and strength training, are inappropriate for improving the function of the stabilising muscles of the lumbar spine.
The most effective exercises for the stabilising muscles need to be very specific and will depend on the patient’s specific condition and stage of recovery.
The other important aspect is that it is very difficult to palpate or feel these muscles when assessing muscle function. It is also difficult for patients with low back pain to feel their own stabilising muscles when they are trying to contract them.
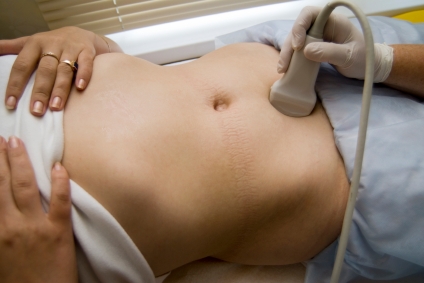
The Role of Real-Time Ultrasound Imaging
This is where RTU imaging comes to the fore. The imaging enables the physiotherapist to view the function of the stabilising muscles “live and in real-time” as the patient contracts them. This gives the therapist and the patient invaluable information as to the quality, timing and endurance of the stabilising muscle contraction. The therapist can then quantify the extent of the dysfunction of the muscle and establish the severity of a patient’s condition.
Since the patient may also view the video image of the muscle contraction as it occurs, RTU imaging can be an effective method of teaching the correct exercise techniques. Actually seeing the muscle as it contracts and feeling the sensation of a correct contraction technique is a powerful form of biofeedback and can speed up the rehabilitation of these critical muscles.
The RTU Imaging Service at Complete Wellness Physiotherapy
The RTU imaging service provides a neat fit with our Clinical Pilates programme. The use of RTU provides an accurate assessment of the patient’s stabilising muscle function. Thus it facilitates, in combination with Clinical Pilates, an effective treatment to improve function.
Most patients with low back pain will require several RTU imaging sessions to ensure correct function of their stabilising muscles, as their exercises are progressed.
For patients participating in a Clinical Pilates programme, RTU can be included as part if the programme, used as an adjunct to the programme or provide an independent assessment at key intervals during the programme.
Some Critical Facts About Low Back Pain
- 80% of people aged between 20 and 50 will experience an episode of low back pain.
- 80% of these will recover after approximately six weeks. The remaining 20% will go on to develop chronic low back pain.
- 80% of those who recover within six weeks will experience another episode of low back pain within 12 months.
- After the second episode of pain, that person is more likely to experience more frequent and more severe exacerbations of pain with time.
- Recent research demonstrates that correct and effective retraining of the deep stabilising muscles following an episode of low back pain, versus patients rehabilitated with standard exercise programmes, decreases the chance of recurrence of low back pain within a two year period by more than 13 times



Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!